Water-softening is an important process for most households and industries, especially where hard water dominates. Hard water is water containing high levels of minerals like calcium and magnesium, responsible for the formation of scales on plumbing and appliances that render soaps and cleaning detergents less effective and cause unsightly spots on dishes and fixtures. Resin is essential to the process of softening water. This blog will explain what exactly resin is,
how it works in water softeners, and the benefits it brings to households and industries alike
Understand Water Softener Resin
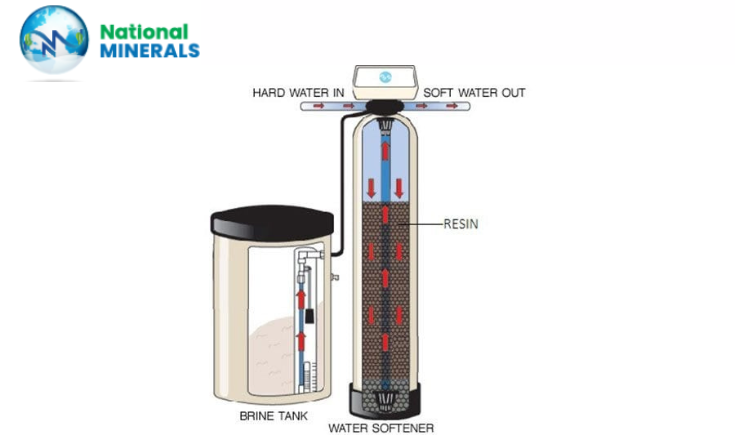
Resin in water softeners is usually made up of small, bead-like material composed of polystyrene that is highly porous. These resin beads come charged with sodium ions, a requirement for the ion exchange process that underlines the water softening mechanism. The beads are contained in a resin tank through which hard water flows during the softening process.
The Ion Exchange Process:
Hard Water Entering the Softener: Hard water flows into the softener and passes through a bed of resin.
Ion Exchange Takes Place: As a result of the hard water flowing around the resin beads, the calcium and magnesium ions of the water are then attracted to and cling to the resin. In return, sodium ions are released from the resin into the water.
Soft Water Leaves the Softener: The water that leaves the softener now has reduced levels of calcium and magnesium and increased levels of sodium and is, therefore, "soft."
This, in effect, reduces the water hardness, thus avoiding scale buildup and improving the effectiveness of soaps and detergents.
Regeneration of Resin
Gradually, calcium and magnesium ions begin to fill up the active sites in the resin beads until it cannot soften the water further. Therefore, such resins require periodic regeneration to regain their water-softening ability. The process follows a regeneration cycle which includes the following steps:
Backwashing would involve rinsing the resin bed to clear it of all the debris or sediment. In the brine draw stage, a very concentrated salt, typically sodium chloride is drawn into the resin tank. As shown in this brine solution is a high concentration of sodium ions, which replace calcium and magnesium ions on the resin beads.
Rinse: The resin bed is rinsed with water for discharging the displaced calcium and magnesium ions along with excess brine solution.
Recharge: Recharge of resin beads with sodium ions so that they can again be used for water softening.
Benefits of Using Resin in Water Softeners
1. Effective Removal of Hardness
Resin beads do a real fine job in filtering off the calcium and magnesium ions from hard water. This ability ensures that the water emerging from the softener is adequately softened for the protection of plumbing and appliances from scale buildup, hence improving the effectiveness of cleaning agents.
2. Longevity and Durability
High-quality resin beads can be used continuously for several years,
even up to a decade, if properly maintained and they are put through a regular regeneration cycle. This makes them cost-effective for water softening.
3. Same Performance
The resin water softener provides the same performance right through. Provided that the resins are recharged from time to time, this device will go on giving you soft water.
4. Low Maintenance
Systems with resin beds, however, require little maintenance. The major maintenance requirements for these systems involve making sure that an adequate quantity of salt is present to recharge the system. There are also systems that make the regeneration cycle completely automatic, making the process nearly hands-free for the user.
5. More Excellent Water Quality
Using resin in the water softener has greatly improved the quality of water. The benefits include soft water that does not build scales, but also helps in keeping the skin softer after bathing, with positive effects on the durability of clothes and the taste of food and drinks made from soft water.
Like this, in a water softener, resin facilitates the ion exchange process and removes the hardness from water to provide better quality. Its resilience and low-maintenance cost make this a very cost-effective solution both for residential and industrial purposes. With advancements in technology, resin beads have become even more efficient and long-lasting.
National Minerals deals in superior quality resin solutions that effectively soften water, hence giving life to the plumbing system and generally improving the overall quality of water. With a focus on innovative and green solutions, we are able to be a trustworthy partner in delivering reliable water treatment solutions.
Activation
Objective: The activation process increases the surface area of the charcoal and forms a network of pores inside that increase its adsorption capabilities. There exist two methods of activation: physical and chemical.
Physical Activation:
Process: Put the charcoal in an activation furnace and heat it to temperatures between 800°C and 1100°C in the presence of some oxidizing agent like steam or carbon dioxide.The high temperature and oxidizing agent create a porous structure within the charcoal.
Result: The steam or carbon dioxide would react with the carbon atoms in the charcoal to give a highly porous material of large surface area.
Chemical Activation:
Procedure: Mix charcoal with a chemical activating agent like phosphoric acid, potassium hydroxide, or zinc chloride. After that, this mixture is to be heated in temperatures varying from 400°C to 700°C.
Process: During this process, the chemical agent will develop the pore structure inside the charcoal. The mixture will be washed properly after activation to remove residual chemicals.
The activated charcoal is washed with deionized water until the wash water is neutral and then dried at a temperature of about 110°C. This step is undertaken to ensure that the impurities and residual chemicals are eliminated.
Final Screening and Packaging
Objective:Ensure uniform size of activated carbon and ready to use.
Method: Finally, pass the activated charcoal through a last sieve for classifying particles by size. This then homogenizes it and makes it appropriate for different uses.
Process: Pack the reworked activated carbon in hermetically sealed containers or bags to retain quality and prevent contamination.
Result: Activated carbon ready to be used in different applications is obtained from coconut shells.
Uses of Activated Carbon
The versatility of coconut shell-based activated carbon is very high, and multiple applications are obtainable, such as:
Water Purification: Removes impurities, chlorine, and organic compounds from drinking water.
Air Filtration: Adsorbs odors, gasses, and volatile organic compounds for use in air purifiers and HVAC systems.
Medical Application: Poisons and overdoses are treated by adsorbing the toxins in the gastrointestinal tract.
Cosmetics: It is used in face masks and scrubs because of its detoxifying features.
Industrial Processes: This is used in the purification of gasses and liquids in chemical processing, food and beverage production, and pharmaceutical industries.
National Minerals is just one of the pioneers in this environment-friendly process for producing activated carbon from coconut shells. By addressing this sustainability factor, National Minerals does not merely recycle wastes but also provides an efficient and environment-friendly adsorbent for industries.